Test Station for Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis
Research - Jul 16, 2024
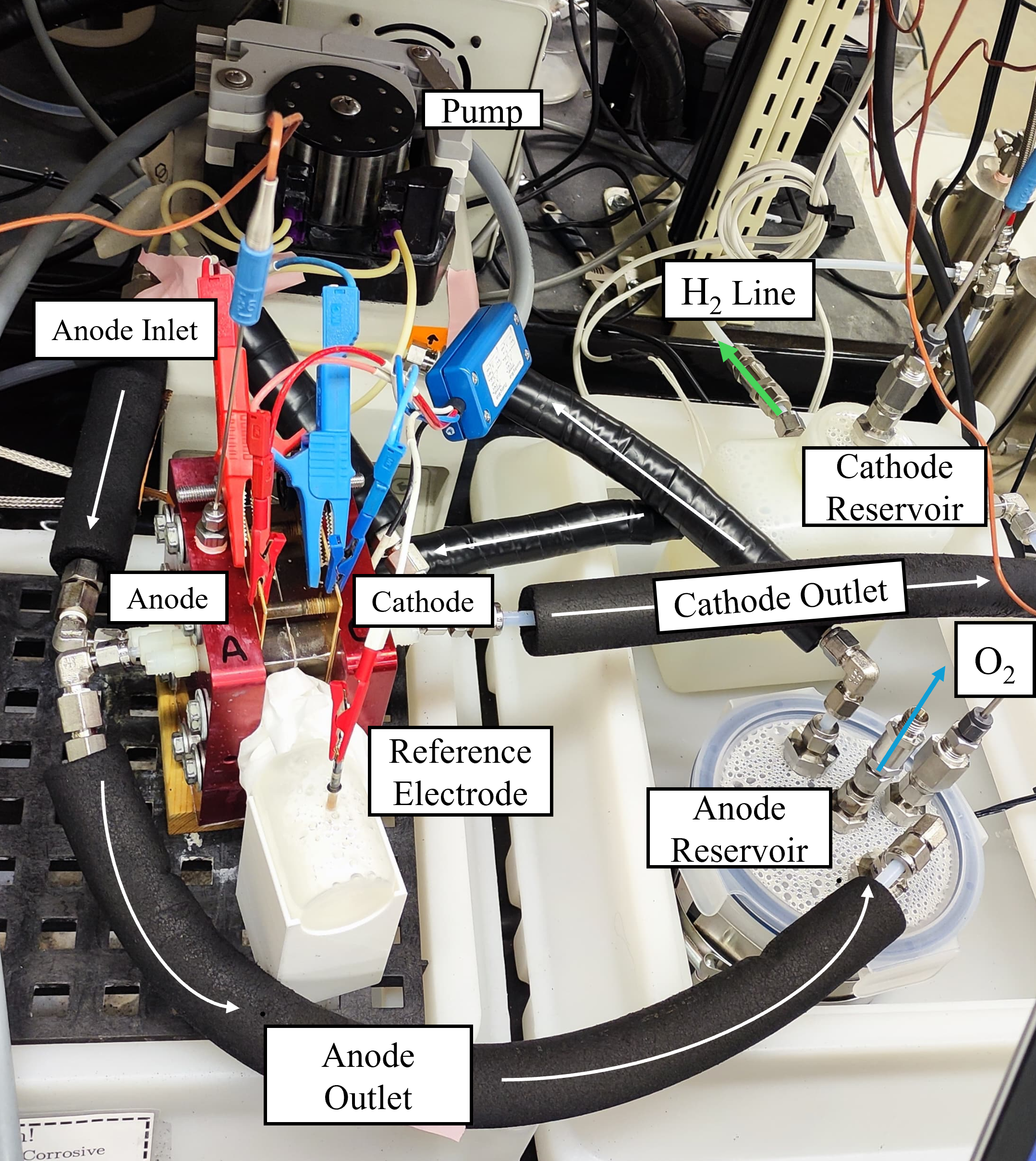
Recent developments in anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) cell materials have allowed for cells to be operated at higher performance levels for longer periods of time. There has not, however, been much consideration of the optimal method for feeding the reactant water, usually in the form of an electrolyte solution. At the ESDLab, we developed the construction and testing of anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) cells to study the effect of electrolyte feed method: Anode-only feed, Cathode-only feed, and Two-electrode feed.
Most recently, we have begun testing on different catalyst loadings for enhancing the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) on the cathode side, and comparing the MEAs (membrane electrode assemblies) methods of Catalyst-coated membranes (CCM) and Catalyst-coated substrates (CCS). This is achieved by the characterization of inks for in-house fabricated CCMs, by inkjet printing catalyst layers onto Aemion+ membranes, which allowed for precise control in the deposition of catalyst layer materials (Platinum carbon for the Cathode, and Iridium oxide for the Anode).
Additionally, the use of a reference electrode is being included in most recent works to measure and understand the overpotentials of the separate half-reactions.